Introduction
Position sizing is a crucial risk management technique used by traders and investors to determine how much of their capital they should allocate to a single trade or investment. Proper position sizing helps in controlling risk exposure and ensuring that no single position can significantly impact the overall portfolio.
Why Position Sizing Matters
Position sizing is essential because it:
- Limits Risk Per Trade: Ensures that even if a trade goes against you, the loss is manageable and does not deplete your account significantly.
- Prevents Overexposure: Protects against allocating too much capital to one position, which could lead to large losses.
- Maintains Portfolio Balance: Helps in diversifying risk by spreading investments across different positions.
Key Factors in Determining Position Size
- Account Size: The total amount of capital in the trading or investment account. Position sizing decisions should be based on a percentage of the overall account balance to maintain risk within acceptable levels.
- Risk Per Trade: The percentage of the account that you are willing to risk on each trade. For instance, a common rule is to risk only 1-2% of the total account on a single trade. If you have a $10,000 account and are willing to risk 2%, you should not risk more than $200 on any given trade.
- Stop-Loss Level: This is the price at which you will exit the trade if it moves against you. The stop-loss helps calculate how much you would potentially lose if the trade hits that level. The distance between your entry price and the stop-loss price determines how many units (shares, contracts, etc.) you can buy or sell.
How to Calculate Position Size
The basic formula for calculating position size is:

Example Calculation:
- Assume your trading account size is $10,000.
- You decide to risk 1% of your account per trade. This means the maximum loss you are willing to accept is $100.
- If you identify a trade with a stop-loss that is $5 away from your entry price, the calculation would be:
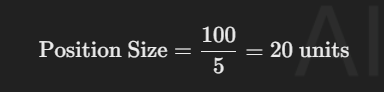
In this example, you would buy 20 units of the asset. This way, if the price hits your stop-loss, you would only lose $100, which is 1% of your account.
Types of Position Sizing Strategies
- Fixed Dollar Amount: A specific dollar amount is risked on each trade. This method is simple but may not adapt well as your account grows or shrinks.
- Fixed Percentage: A set percentage of your account is risked per trade. This method adjusts the position size according to the account balance, maintaining consistent risk exposure.
- Volatility-Based Position Sizing: Adjusts the position size based on the volatility of the asset. Higher volatility leads to smaller position sizes to manage risk effectively, and lower volatility allows for larger positions.
Benefits of Position Sizing
- Reduces Emotional Trading: By predetermining position sizes, traders are less likely to make impulsive decisions based on emotions.
- Preserves Capital: Ensures that a series of losing trades does not significantly impact the account balance.
- Enables Consistent Risk Management: Helps maintain a uniform approach to risk across all trades, making the strategy more sustainable over the long term.
Position Sizing Tools
Many trading platforms offer built-in tools to calculate position sizes. Traders can also use spreadsheet templates or specialized position sizing calculators available online to simplify this process.
Summary
Position sizing is an essential component of risk management that determines how much capital should be allocated to each trade. By taking into account account size, risk per trade, and stop-loss levels, traders can manage their exposure and protect their portfolios from significant losses. Consistent use of position sizing contributes to disciplined trading and long-term financial health.


Leave a Reply